
Back to top
Antisense Oligos

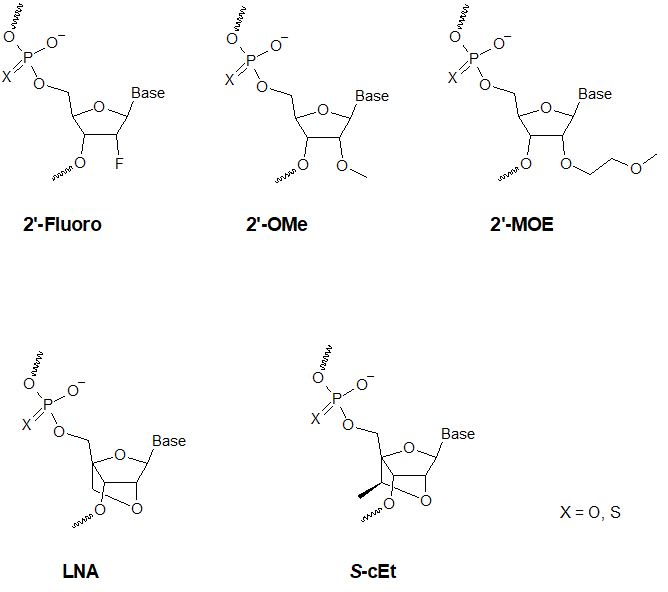
- 2'-O-Methyl
- 2'-Fluoro
- MOE (2'-methoxyethyl)
- LNA (locked nucleic acid)
- S-cEt (constrained ethyl, on request)
- PTO (phosphorothioate)
- Gapmers
- GalNAc
Features and Benefits
- All ASOs are MALDI-TOF MS controlled before shipment
- Microsynth is a renowned ASO supplier to top research institutes and pharma/biotech companies
- Low endotoxin oligonucleotides are available on request
- Synthesis scales up to 15 µmol including HPLC are shipped within just 4-6 days
- For in vivo applications production times from just 3 weeks including endotoxin testing
- Well-trained and highly experienced scientists are ready to support you
- Competitive pricing
- High guaranteed yields
- Analytical HPLC available
- Certificate of Analysis available
- Easy-to-use online portal with a series of helpful tools (e.g. order tracking & history, convenient search and re-order option)
Overview
-
PTO (phosphorothioates) modifications: PTOs contain one sulfur atom in place of an oxygen atom in the internucleotide linkage of DNA or RNA. This modification of the normal phosphodiester backbone is characterized by an increased cell uptake, high nuclease resistance and elicitation of RNase H activity.
- 2'-O-Me-RNA modifications: The incorporation of 2'-O-Methyl RNA nucleotides induces a resistance to a wide variety of nucleases, in particular, RNase. Furthermore, 2’-OMe oligonucleotides show a slightly increased affinity towards their complementary mRNA target sequence, thereby forming more stable hybrid duplexes compared to their non-modified DNA or RNA counterparts. This enables the formation of more stable hybrids with complementary RNA strands than would be the case for non-modified DNA and RNA sequences.
-
2'-MOE-RNA modifications: Oligonucleotides incorporating 2'-O-methoxyethyl (MOE)-modified nucleotides, can support most, if not all antisense mechanisms of action. Further key distinctive characteristics are nuclease resistance, lower toxicity, superior target binding specificity, as well as an increased affinity towards complementary RNA. For more detailed information about 2'-MOE antisense oligonucleotides from Microsynth, please refer to the flyer on the right-hand side.
-
LNA modifications: LNA containing oligonucleotides offer substantially increased affinity for its complementary strand, compared to traditional DNA or RNA oligonucleotides. This and the concomitant high nuclease resistance of LNAs results in unprecedented sensitivity and specificity and makes LNA™ oligonucleotides ideal for use in antisense applications.
- S-cEt modifications: S-cEt oligonucleotides (constrained ethyl nucleotides) are an advancement of LNA oligonucleotides. They have been developed for antisense applications and are mainly used in gapmers. Such ASOs show superior stability towards nuclease degradation compared to LNA without compromising binding selectivity or hybridization stability.
- N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc): Conjugation of N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc) has become a major clinical strategy for the delivery of oligonucleotides to hepatocytes (liver cells). Such conjugates are efficiently internalized by binding to the asialoglycoprotein receptor (ASGPR), which exhibits high affinity for N-acetyl galactosamine terminated oligosaccharides.
To learn more about the specifications of these five types of modifications, please see the table below.
Key Specifications:
|
Modifications |
Position |
Synthesis scale [µmol] | Purification1 | |||||
|
5’ |
3’ |
Int. |
0.04 |
0.2 |
1 |
15 |
HPLC + Dialysis |
|
|
PTO |
x |
x |
x |
x |
x |
x |
||
| 2’-O-Me-RNA |
x |
x |
x |
x |
x |
x |
x |
x |
| 2'-MOE-RNA | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| LNA | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| GalNAc | x | x | x | x | x | |||
1 We strongly recommend to order ASOs with “HPLC + Dialysis” purification. The Na+ salt exchange is necessary to remove toxic salts from HPLC purification. For in vivo testing we recommend our low endotoxin oligonucleotides.
Synthesis Scales
Full 2' OMe, 2' MOE in combination with or without PTO
Desalted
| Synthesis scale1 | Length Restriction | Guaranteed Yield2 | Production Time [wd] | |
| [OD260] | [nmol]3 | |||
| 0.04 µmol | 13 - 30 | 3 | 15 | 2-3 |
| 0.2 µmol | 10 | 50 | 2-3 | |
| 1.0 µmol | 30 | 150 | 2-3 | |
| 15 µmol | 600 | 3'000 | 3-5 | |
HPLC
| Synthesis scale1 | Length Restriction | Guaranteed Yield2 | Production Time [wd] | |
| [OD260] | [nmol]3 | |||
| 0.04 µmol | 13 - 30 | 1 | 5 | 3-4 |
| 0.2 µmol | 3 | 15 | 3-4 | |
| 1.0 µmol | 10 | 50 | 3-4 | |
| 15 µmol | 300 | 1'500 | 4-6 | |
HPLC & Dialysis
| Synthesis scale1 | Length Restriction | Guaranteed Yield2 | Production Time [wd] | |
| [OD260] | [nmol]3 | |||
| 0.04 µmol | 13 - 30 | - | - | - |
| 0.2 µmol | 3 | 15 | 3-5 | |
| 1.0 µmol | 10 | 50 | 3-5 | |
| 15 µmol | 250 | 1'250 | 5-7 | |
PAGE
| Synthesis scale1 | Length Restriction | Guaranteed Yield2 | Production Time [wd] | |
| [OD260] | [nmol]3 | |||
| 0.04 µmol | 13 - 30 | 0.5 | 2.5 | 3-4 |
| 0.2 µmol | 2 | 10 | 3-4 | |
| 1.0 µmol | 7 | 35 | 3-4 | |
| 15 µmol | - | - | - | |
Gapmers (including DNA and 2' OMe or 2' MOE)
HPLC
| Synthesis scale1 | Length Restriction | Guaranteed Yield2 | Production Time [wd] | |
| [OD260] | [nmol]3 | |||
| 0.04 µmol | 13 - 30 | 1 | 5 | 3-4 |
| 0.2 µmol | 3 | 15 | 3-4 | |
| 1.0 µmol | 8 | 40 | 3-4 | |
| 15 µmol | 300 | 1'500 | 4-6 | |
HPLC & Dialysis
| Synthesis scale1 | Length Restriction | Guaranteed Yield2 | Production Time [wd] | |
| [OD260] | [nmol]3 | |||
| 0.04 µmol | 13 - 30 | - | - | - |
| 0.2 µmol | 3 | 15 | 3-5 | |
| 1.0 µmol | 8 | 40 | 3-5 | |
| 15 µmol | 250 | 1'250 | 5-7 | |
PAGE
| Synthesis scale1 | Length Restriction | Guaranteed Yield2 | Production Time [wd] | |
| [OD260] | [nmol]3 | |||
| 0.04 µmol | 13 - 30 | 0.5 | 2.5 | 3-4 |
| 0.2 µmol | 2 | 10 | 3-4 | |
| 1.0 µmol | 7 | 35 | 3-4 | |
| 15 µmol | - | - | - | |
Gapmers (including DNA and LNA)
HPLC
| Synthesis scale1 | Length Restriction | Guaranteed Yield2 | Production Time [wd] | |
| [OD260] | [nmol]3 | |||
| 0.04 µmol | 13 - 30 | 1 | 5 | 3-4 |
| 0.2 µmol | 2 | 10 | 3-4 | |
| 1.0 µmol | 6 | 30 | 3-4 | |
| 15 µmol | 250 | 1'250 | 4-6 | |
HPLC & Dialysis
| Synthesis scale1 | Length Restriction | Guaranteed Yield2 | Production Time [wd] | |
| [OD260] | [nmol]3 | |||
| 0.04 µmol | 13 - 30 | - | - | - |
| 0.2 µmol | 2 | 10 | 3-5 | |
| 1.0 µmol | 6 | 30 | 3-5 | |
| 15 µmol | 200 | 1'000 | 5-7 | |
PAGE
| Synthesis scale1 | Length Restriction | Guaranteed Yield2 | Production Time [wd] | |
| [OD260] | [nmol]3 | |||
| 0.04 µmol | 13 - 30 | 0.5 | 2.5 | 3-4 |
| 0.2 µmol | 2 | 10 | 3-4 | |
| 1.0 µmol | 5 | 25 | 3-4 | |
| 15 µmol | - | - | - | |
How to Order
- Enter our webshop
- Click on DNA in the blue "DNA/RNA Synthesis" domain
- Select either Normal Entry in order to type or copy/paste the desired sequence information etc. or alternatively select Upload Entry by using our convenient Excel template (can be downloaded from our webshop).
- Enter 5,6,7,8 for each distinct base to be replaced inside the sequence
- Define Inner Modification (5=…) by selecting the desired modification from the drop down menu (e.g. 5=…2’-O-Methyl-RNA-A, 6=…2’-O-Methyl-RNA-C etc.)
- Enter 5,6,7,8 for each distinct base to be replaced inside the sequence
- Define Inner Modification (5=…) by selecting the desired modification from the drop down menu (e.g. 5=…2’-Methoxyethyl-ribo-A, 6=…2’-Methoxyethyl-ribo-mC etc.)
-
Enter 5,6,7,8 for each distinct base to be replaced inside the sequence
-
Define Inner Modification (5=…) by selecting the desired modification from the drop down menu (e.g. 5=…LNA-A, 6=…LNA-C etc.)
- cEt ASO are available on request only. Ordering instructions follow together with the offer.
Low Endotoxin Oligonucleotides
- Low endotoxin ASOs are available on request only. Ordering instructions follow together with the offer.

