Back to top
Functional Groups (for ADN)
|
Functional Groups
|
Position
|
||
|
|
5’
|
3’
|
int
|
| Alkyne |
|
X
|
|
| Amino / Amino-dT |
X
|
X
|
X
|
| Azide / Azide-dT |
X
|
X
|
X
|
| DBCO / DBCO-dT |
X
|
|
X
|
| Hexynyl |
X
|
|
|
| Phosphate |
X
|
X
|
|
| Phosphorothioate (PTO) |
|
|
X
|
| Thiol |
X
|
X
|
|
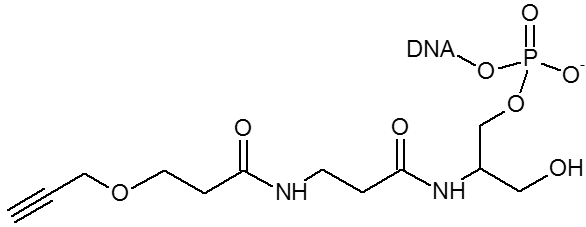
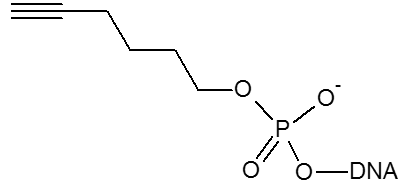
The alkyne group is used for copper assisted cycloaddition click chemistry.
|
Position
|
Echelle de Synthèse [µmol]
|
Purification
|
|||||
|
|
0.04
|
0.2
|
1.0
|
15
|
Des
|
HPLC
|
PAGE
|
| 3' |
X
|
X
|
O |
X
|
X | ||
Amino / Amino-dT
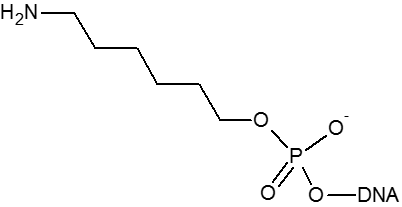
A primary amino group can be used to attach a variety of modifiers (such as fluorescent dyes) to an oligonucleotide or used to attach an oligonucleotide to a solid surface. Amino modifiers can be positioned at the 5’-end with either a standard (C6) or longer (C12) spacer arm. Amino modifications can be positioned at the 3’-end. Internal amino modifications can be introduced using an amino-dT base.
|
Groupes Fonctionnels
|
Position
|
Echelle de Synthèse [µmol]
|
Purification
|
|||||
|
|
0.04
|
0.2
|
1.0
|
15
|
Des
|
HPLC
|
PAGE
|
|
| Amino C6 |
5’
|
X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
|
3’
|
X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |
|
Amino C6-dT
|
Int
|
|
X | X | O |
|
X | X |
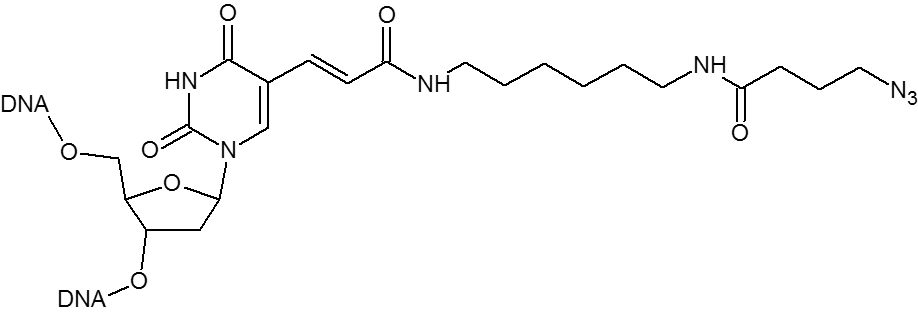
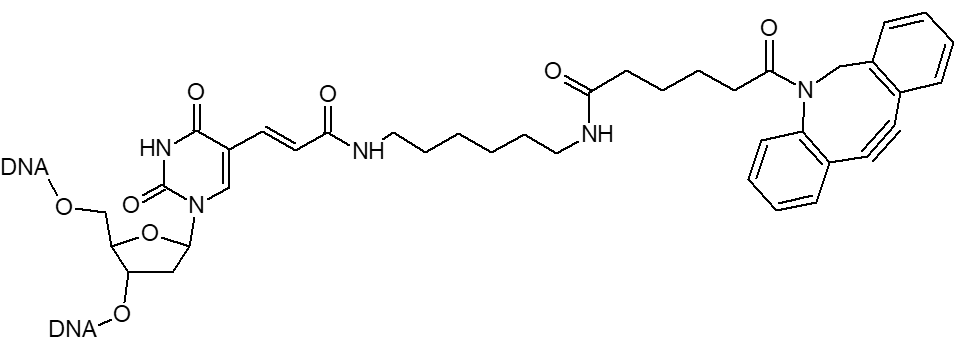
Azide / Azide-dT
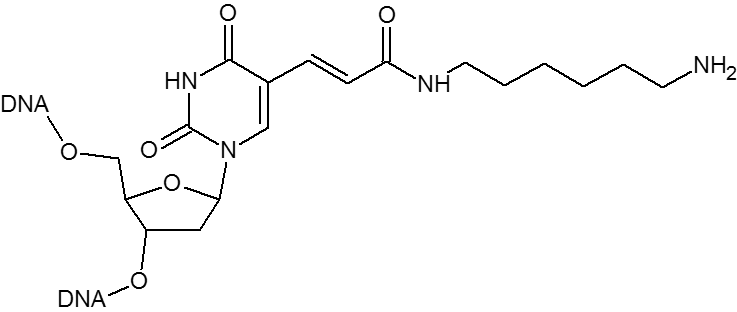
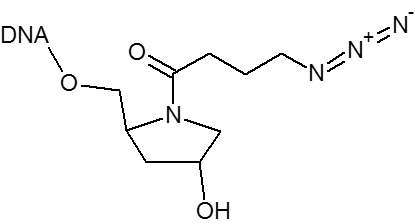
Microsynth's Azide modification uses an NHS Ester functional group to attach an azide moiety at the 5', 3' or any internal position in an oligo. This azide moiety may subsequently be used to attach alkyne modified groups through the click reaction. The internal version of this modification is attached to the oligo through a dT base. Incorporation of the internal version will add a dT nucleotide at that position. To avoid adding an extra nucleotide, replace an existing T nucleotide in your sequence with the required modification.
|
Groupes Fonctionnels
|
Position
|
Echelle de Synthèse [µmol]
|
Purification
|
|||||
|
|
0.04
|
0.2
|
1.0
|
15
|
Des
|
HPLC
|
PAGE
|
|
| Azide |
5’
|
X | X | O | X | X | ||
|
3’
|
X | X | O | X | X | |||
|
Azide-dT
|
Int
|
|
X | X | O | X | X | |
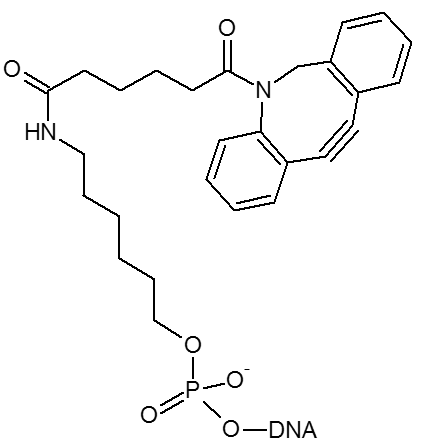
DBCO / DBCO-dT
DBCO est un modificateur à base de cyclooctyne pour les réacctions click avec le cuivre.
|
Groupes Fonctionnels
|
Position
|
Echelle de Synthèse [µmol]
|
Purification
|
|||||
|
|
0.04
|
0.2
|
1.0
|
15
|
Des
|
HPLC
|
PAGE
|
|
| DBCO |
5’
|
X | X | O | X | |||
|
3’
|
||||||||
|
DBCO-dT
|
Int
|
|
X | X | O | X | ||
Le groupe Hexynyl 5' est utilisé pour la cycloaddition assistée par le cuivre. Les oligonucléotides préparés à l'aide de phosphoramidite de 5'-hexynyl sont stables dans des conditions de dé-protection standard et présentent un temps de rétention légèrement accru sur la RP HPLC.
|
Position
|
Echelle de Synthèse [µmol]
|
Purification
|
|||||
|
|
0.04
|
0.2
|
1.0
|
15
|
Des
|
HPLC
|
PAGE
|
| 5' |
X
|
X
|
O |
X
|
X | ||
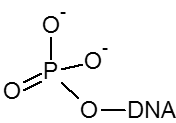
La phosphorylation en 5' est nécessaire si un oligo est utilisé comme substrat pour l'ADN ligase. La phosphorylation 3' inhibe la dégradation par certaines exonucléases 3' et peut être utilisée pour bloquer l'élongation par les polymérases de l'ADN.
|
Position
|
Echelle de Synthèse [µmol]
|
Purification
|
|||||
|
|
0.04
|
0.2
|
1.0
|
15
|
Des
|
HPLC
|
PAGE
|
| 5' | X |
X
|
X
|
X | X |
X
|
X |
| 3' | - |
X
|
X
|
- | X |
X
|
X |
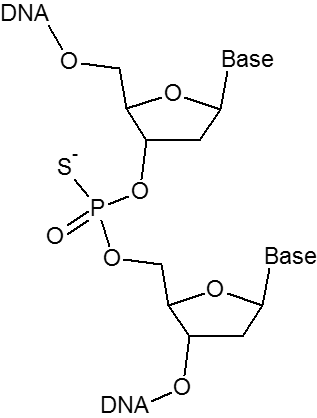
La liaison phosphorothioate (PTO) remplace un atome de soufre par un oxygène non pontant dans le squelette phosphate d'un oligo. Cette modification rend la liaison inter-nucléotidique résistante à la dégradation par les nucléases. Des liaisons phosphorothioate peuvent être introduites entre les 3-5 derniers nucléotides à l'extrémité 5' ou 3' de l'oligo pour inhiber la dégradation par les exonucléases. L'inclusion de liaisons phosphorothioate dans l'ensemble de l'oligo contribuera également à réduire l'attaque par les endonucléases.
|
Position
|
Echelle de Synthèse [µmol]
|
Purification
|
|||||
|
|
0.04
|
0.2
|
1.0
|
15
|
Des
|
HPLC
|
PAGE
|
| Int | X |
X
|
X
|
X | X |
X
|
X |
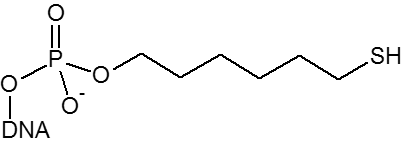
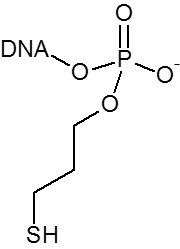
Thiol
|
Position
|
Echelle de Synthèse [µmol]
|
Purification
|
|||||
|
|
0.04
|
0.2
|
1.0
|
15
|
Des
|
HPLC
|
PAGE
|
| 5' |
X
|
X
|
X |
X
|
X | ||
| 3' |
X
|
X
|
O |
X
|
X | ||