Back to top
Functional Groups (for DNA)
|
Functional Groups
|
Position
|
||
|
|
5’
|
3’
|
int
|
| Alkyne |
|
X
|
|
| Amino / Amino-dT |
X
|
X
|
X
|
| Azide / Azide-dT |
X
|
X
|
X
|
| DBCO / DBCO-dT |
X
|
|
X
|
| Hexynyl |
X
|
|
|
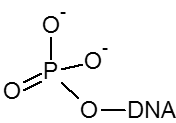
| Phosphate |
X
|
X
|
|
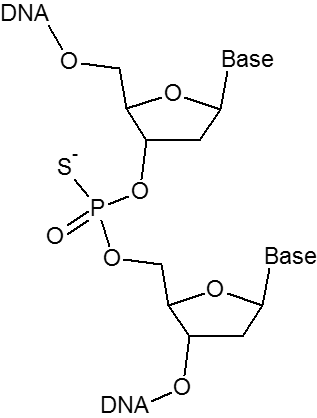
| Phosphorothioate (PTO) |
|
|
X
|
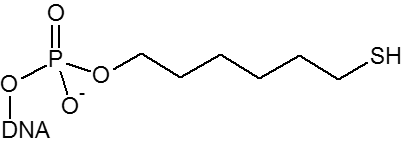
| Thiol |
X
|
X
|
|
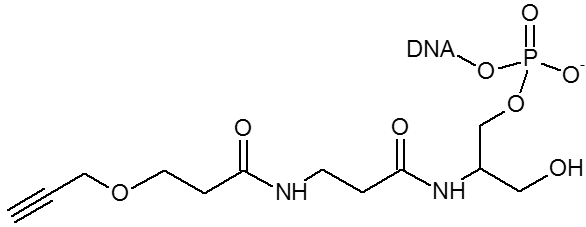
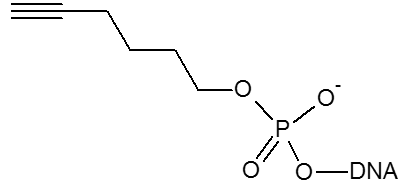
The alkyne group is used for copper assisted cycloaddition click chemistry.
|
Position
|
Synthesis Scale [µmol]
|
Purification
|
|||||
|
|
0.04
|
0.2
|
1.0
|
15
|
Des
|
HPLC
|
PAGE
|
| 3' |
X
|
X
|
O |
X
|
X | ||
Amino / Amino-dT
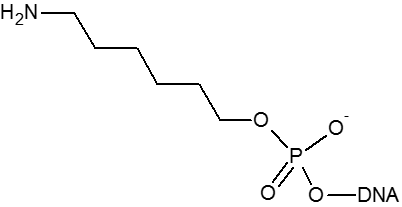
A primary amino group can be used to attach a variety of modifiers (such as fluorescent dyes) to an oligonucleotide or used to attach an oligonucleotide to a solid surface. Amino modifiers can be positioned at the 5’-end with either a standard (C6) or longer (C12) spacer arm. Amino modifications can be positioned at the 3’-end. Internal amino modifications can be introduced using an amino-dT base.
|
Functional Group
|
Position
|
Synthesis Scale [µmol]
|
Purification
|
|||||
|
|
0.04
|
0.2
|
1.0
|
15
|
Des
|
HPLC
|
PAGE
|
|
| Amino C6 |
5’
|
X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
|
3’
|
X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |
|
Amino C6-dT
|
Int
|
|
X | X | O |
|
X | X |
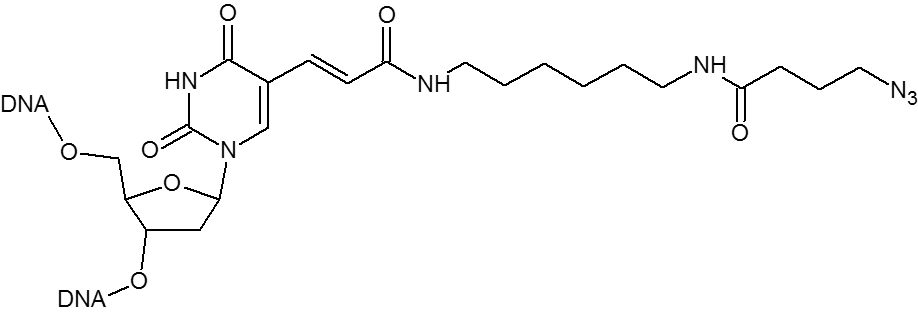
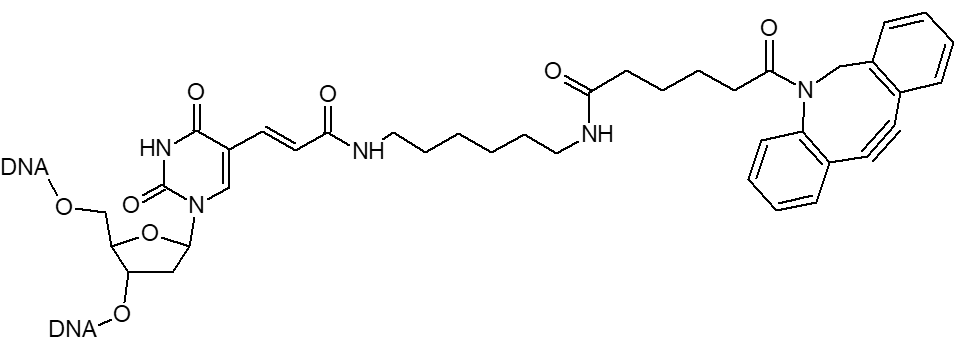
Azide / Azide-dT
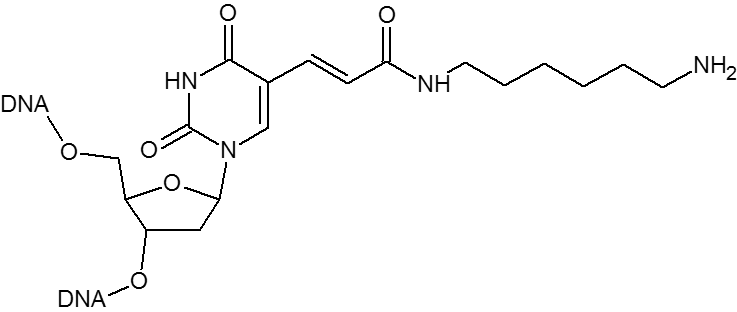
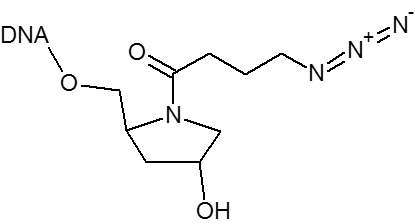
Microsynth's Azide modification uses an NHS Ester functional group to attach an azide moiety at the 5', 3' or any internal position in an oligo. This azide moiety may subsequently be used to attach alkyne modified groups through the click reaction. The internal version of this modification is attached to the oligo through a dT base. Incorporation of the internal version will add a dT nucleotide at that position. To avoid adding an extra nucleotide, replace an existing T nucleotide in your sequence with the required modification.
|
Functional Group
|
Position
|
Synthesis Scale [µmol]
|
Purification
|
|||||
|
|
0.04
|
0.2
|
1.0
|
15
|
Des
|
HPLC
|
PAGE
|
|
| Azide |
5’
|
X | X | O | X | X | ||
|
3’
|
X | X | O | X | X | |||
|
Azide-dT
|
Int
|
|
X | X | O | X | X | |
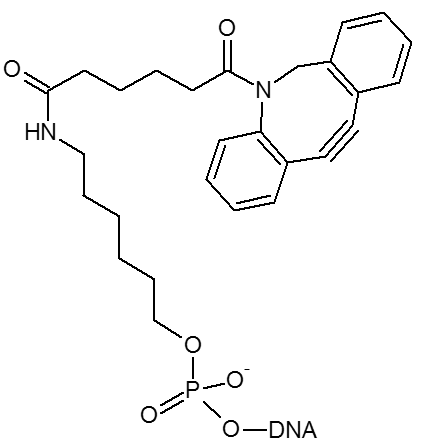
DBCO / DBCO-dT
DBCO is a cyclooctyne-based modifier for copper free click.
|
Functional Group
|
Position
|
Synthesis Scale [µmol]
|
Purification
|
|||||
|
|
0.04
|
0.2
|
1.0
|
15
|
Des
|
HPLC
|
PAGE
|
|
| DBCO |
5’
|
X | X | O | X | |||
|
3’
|
||||||||
|
DBCO-dT
|
Int
|
|
X | X | O | X | ||
The 5' Hexynyl group is used for copper assisted cycloaddition click chemistry. Oligonucleotides prepared using 5'-Hexynyl Phosphoramidite are stable to standard deprotection conditions and exhibit a slightly increased retention time on RP HPLC.
|
Position
|
Synthesis Scale [µmol]
|
Purification
|
|||||
|
|
0.04
|
0.2
|
1.0
|
15
|
Des
|
HPLC
|
PAGE
|
| 5' |
X
|
X
|
O |
X
|
X | ||
5’ Phosphorylation is needed if an oligo is used as a substrate for DNA ligase. 3’ Phosphorylation will inhibit degradation by some 3’-exonucleases and can be used to block extension by DNA polymerases.
|
Position
|
Synthesis Scale [µmol]
|
Purification
|
|||||
|
|
0.04
|
0.2
|
1.0
|
15
|
Des
|
HPLC
|
PAGE
|
| 5' | X |
X
|
X
|
X | X |
X
|
X |
| 3' | - |
X
|
X
|
- | X |
X
|
X |
The phosphorothioate (PTO) bond substitutes a sulfur atom for a non-bridging oxygen in the phosphate backbone of an oligo. This modification renders the internucleotide linkage resistant to nuclease degradation. Phosphorothioate bonds can be introduced between the last 3-5 nucleotides at the 5'- or 3'-end of the oligo to inhibit exonuclease degradation. Including phosphorothioate bonds throughout the entire oligo will help reduce attack by endonucleases as well.
|
Position
|
Synthesis Scale [µmol]
|
Purification
|
|||||
|
|
0.04
|
0.2
|
1.0
|
15
|
Des
|
HPLC
|
PAGE
|
| Int | X |
X
|
X
|
X | X |
X
|
X |
|
Position
|
Synthesis Scale [µmol]
|
Purification
|
|||||
|
|
0.04
|
0.2
|
1.0
|
15
|
Des
|
HPLC
|
PAGE
|
| 5' |
X
|
X
|
X |
X
|
X | ||
| 3' |
X
|
X
|
O |
X
|
X | ||