Back to top
Functional Groups (for RNA)
|
Functional Groups
|
Position
|
||
|
|
5’
|
3’
|
int
|
| Amino |
X
|
X
|
X
|
| Phosphate |
X
|
X
|
|
| Phosphorothioate (PTO) |
|
|
X
|
Amino
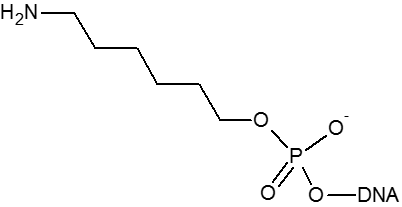
A primary amino group can be used to attach a variety of modifiers (such as fluorescent dyes) to an oligonucleotide or used to attach an oligonucleotide to a solid surface. Amino modifiers can be positioned at the 5’-end with either a standard (C6) or longer (C12) spacer arm. Amino modifications can be positioned at the 3’-end. Internal amino modifications can be introduced using an amino-dT base.
|
Functional Group
|
Position
|
Synthesis Scale [µmol]
|
Purification
|
|||||
|
|
0.04
|
0.2
|
1.0
|
15
|
Des
|
HPLC
|
PAGE
|
|
| Amino C6 |
5’
|
X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
|
3’
|
X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |
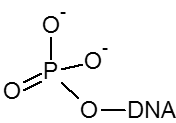
5’ Phosphorylation is needed if an oligo is used as a substrate for DNA ligase. 3’ Phosphorylation will inhibit degradation by some 3’-exonucleases and can be used to block extension by DNA polymerases.
|
Position
|
Synthesis Scale [µmol]
|
Purification
|
|||||
|
|
0.04
|
0.2
|
1.0
|
15
|
Des
|
HPLC
|
PAGE
|
| 5' | X |
X
|
X
|
X | X |
X
|
X |
| 3' | X |
X
|
X
|
O | X |
X
|
X |
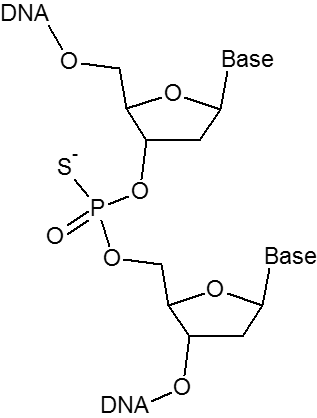
The phosphorothioate (PTO) bond substitutes a sulfur atom for a non-bridging oxygen in the phosphate backbone of an oligo. This modification renders the internucleotide linkage resistant to nuclease degradation. Phosphorothioate bonds can be introduced between the last 3-5 nucleotides at the 5'- or 3'-end of the oligo to inhibit exonuclease degradation. Including phosphorothioate bonds throughout the entire oligo will help reduce attack by endonucleases as well.
|
Position
|
Synthesis Scale [µmol]
|
Purification
|
|||||
|
|
0.04
|
0.2
|
1.0
|
15
|
Des
|
HPLC
|
PAGE
|
| Int | X |
X
|
X
|
X | X |
X
|
X |